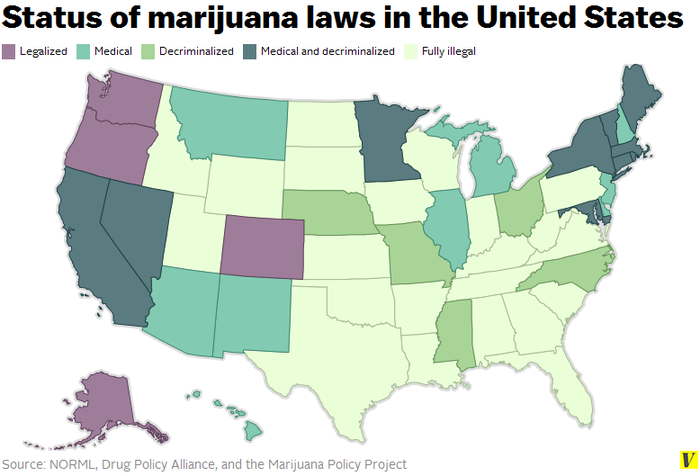
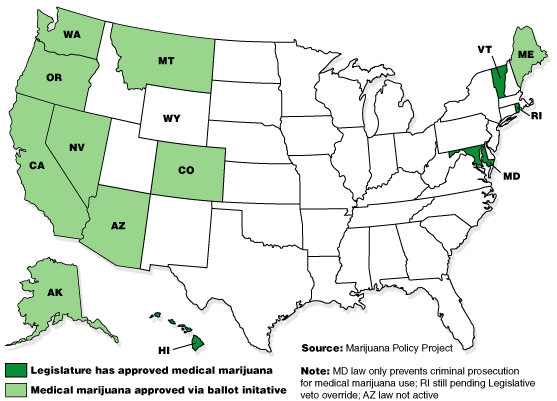
A proposed change to the nation’s rigid drug sentencing laws could save taxpayers billions, according to a new report by the United States Sentencing Commission, the agency that guides sentencing policy for the federal courts.
The report, released Tuesday, examines the impact of a reform that would shave an average of two years off the sentences of roughly half the people serving time in the federal prison system for drug crimes. Doing so would save the government 83,525 “bed years,” the report concludes. (A “bed year” is the bureaucratic term for the cost of keeping one person behind bars for one year.)
With about 100,000 federal prisoners doing time for drugs, at the cost of nearly $30,000 per prisoner a year, that comes out to more than $2.4 billion in total savings.
Recent remarks by Department of Justice officials suggest that they could use every cent. Prison costs make up a third of the department’s budget, and the department’s inspector general has warned that prison overcrowding poses an “increasingly critical threat” to the safety and security of prisoners and staff.
Last month, the seven-member Sentencing Commission voted unanimously to adopt a change to the sentencing guidelines that would reduce drug sentences by an average of about 11 months per prisoner. Unless Congress rejects the change, it will go into effect on Nov. 1. Tuesday’s report considers what would happen if the reform were applied to prisoners who are already behind bars. The commission says it will decide by July 18 whether to make the change retroactive.
Mary Price, an attorney with Families Against Mandatory Minimums, a group that opposes harsh sentencing laws, supports retroactivity “for so many reasons.”
“It would be a cruel irony to fix the problem of over-sentencing only to deny relief to the thousands who have suffered its consequences,” she said in a statement. “It will also make a real impact on the federal prison population, which hovers at nearly 40 percent above capacity and which siphons funds needed for crime prevention, detection and prosecution.”
To understand how the proposed reform would work, one needs to understand something of the history of America’s byzantine sentencing system. In 1986, at the crest of a national wave of concern about crack cocaine, the U.S. adopted a law that assigned specific sentencing levels and penalty ranges to a variety of drug crimes. For example, if someone is convicted of selling 15 grams of meth, that person is considered a “level 18” offender under the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1986, which imposes a recommended sentence for the crime, generally between 27 and 33 months in prison.
The new guidelines adopted by the Sentencing Commission would lower the standard sentencing levels by two points across the board. In this example, a person convicted of selling 15 grams of meth would then be rated a “level 16” offender, resulting in between 21 and 27 months behind bars.
Of the 100,888 people currently in federal prison for drug convictions, only about half would be eligible for a sentence reduction under the reform, should it be applied retroactively. Many of the ineligible prisoners were sentenced under separate mandatory minimum statutes that require they spend a fixed amount of time in prison.
The reform is just one measure that could allow the Department of Justice to trim its bloated prison budget. Congress is considering a bipartisan bill that would reduce mandatory minimum sentences for those convicted of nonviolent drug crimes, and the Justice Department recently announced a huge expansion of its clemency process, which could lead to hundreds of drug prisoners going free before their sentences are up.
(Thanks to reporter Saki Knafo and the HuffPo for this story)