You may not know who Arjan Roskam is, but you’ve probably smoked his ganja. Arjan’s been breeding some of the most famous marijuana strains in the entire world—like White Widow, Super Silver Haze, among others—for over 20 years.
He opened his first “coffee shop” in 1992 in Amsterdam and has since crafted his skills into a market-savvy empire known as Green House Seed Company, which rakes in millions of dollars a year.
He’s won 38 Cannabis Cups and dubbed himself the King of Cannabis.
In this well-researched VICE doc, the crew joins Arjan in Colombia to look for three of the country’s rarest types of weed, strains that have remained genetically pure for decades. They trudge up mountains and crisscross military checkpoints in the country’s still-violent south, and then head north to the breathtaking Caribbean coast. As the dominoes of criminalization fall throughout the world, Arjan is positioned to be at the forefront of the legitimate international seed trade.
About the Author
Michael is a journalist and filmmaker. His award-winning documentary, Sleeping with Siri is playing film festivals across the country. Stusser runs TechTimeout campaigns in high schools across the country, asking teenagers to give up their digital devices (for a little while) in order to find balance, and perhaps even make eye-contact with their parents.You Might also like
-
New York Times Endorses Legalization
By THE EDITORIAL BOARD
It took 13 years for the United States to come to its senses and end Prohibition, 13 years in which people kept drinking, otherwise law-abiding citizens became criminals and crime syndicates arose and flourished. It has been more than 40 years since Congress passed the current ban on marijuana, inflicting great harm on society just to prohibit a substance far less dangerous than alcohol.
The federal government should repeal the ban on marijuana.
We reached that conclusion after a great deal of discussion among the members of The Times’s Editorial Board, inspired by a rapidly growing movement among the states to reform marijuana laws.
There are no perfect answers to people’s legitimate concerns about marijuana use. But neither are there such answers about tobacco or alcohol, and we believe that on every level — health effects, the impact on society and law-and-order issues — the balance falls squarely on the side of national legalization. That will put decisions on whether to allow recreational or medicinal production and use where it belongs — at the state level.
We considered whether it would be best for Washington to hold back while the states continued experimenting with legalizing medicinal uses of marijuana, reducing penalties, or even simply legalizing all use. Nearly three-quarters of the states have done one of these.
But that would leave their citizens vulnerable to the whims of whoever happens to be in the White House and chooses to enforce or not enforce the federal law.
The social costs of the marijuana laws are vast. There were 658,000 arrests for marijuana possession in 2012, according to F.B.I. figures, compared with 256,000 for cocaine, heroin and their derivatives. Even worse, the result is racist, falling disproportionately on young black men, ruining their lives and creating new generations of career criminals.
There is honest debate among scientists about the health effects of marijuana, but we believe that the evidence is overwhelming that addiction and dependence are relatively minor problems, especially compared with alcohol and tobacco. Moderate use of marijuana does not appear to pose a risk for otherwise healthy adults. Claims that marijuana is a gateway to more dangerous drugs are as fanciful as the “Reefer Madness” images of murder, rape and suicide.
There are legitimate concerns about marijuana on the development of adolescent brains. For that reason, we advocate the prohibition of sales to people under 21.
Creating systems for regulating manufacture, sale and marketing will be complex. But those problems are solvable, and would have long been dealt with had we as a nation not clung to the decision to make marijuana production and use a federal crime.
In coming days, we will publish articles by members of the Editorial Board and supplementary material that will examine these questions. We invite readers to offer their ideas, and we will report back on their responses, pro and con.
We recognize that this Congress is as unlikely to take action on marijuana as it has been on other big issues. But it is long past time to repeal this version of Prohibition.
http://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2014/07/27/opinion/sunday/high-time-marijuana-legalization.html?_r=3&smid=tw-share
-
Hillary Should Admit She Didn’t Inhale with Bill
Hillary Clinton is by far the most reasonable Presidential candidate about marijuana policy, but we have a hard time inhaling her non-admission about never trying it. After all, she’s married to…Bill!
-
THE TIDE HAS TURNED
Great article from Josh Voorhees, our favorite SLATE contributor
Courtesy of Slate –
An overwhelming majority of Americans believe that the legalization of marijuana is inevitable. We’ll soon find out if they’re right.
Voters in Alaska and possibly Oregon will decide this November whether their states will join Colorado and Washington in legalizing the commercial sale and recreational use of pot. Similar initiatives are at varying stages in more than a half-dozen other states—Nevada, Arizona, and California among them—where advocates are looking toward 2016, when they hope the presidential election will turn out enough liberals to push those efforts across the finish line. All told, more than 1 in 5 Americans live in states where marijuana use has a legitimate chance to become legal between now and when President Obama leaves office.
It’s not just at the ballot box where the pro-pot crowd is putting points on the board. Lawmakers in at least 40 states have eased at least some drug laws since 2009, according to a recent Pew Research Center analysis. According to the Marijuana Policy Project, proposals to treat pot like alcohol have been introduced in 18 states and the District of Columbia this year alone. Meanwhile, 16 states have already decriminalized marijuana, according to the pro-pot group NORML—Maryland will become the 17th in October. In large swaths of the country getting caught with a small amount of weed at a concert is now roughly the same as getting a speeding ticket on the way to the show. While not leading the charge, the Obama administration is allowing states the chance to experiment. The feds have given a qualified greenlight to Colorado and Washington to dabble in recreational weed, and have even taken small steps to encourage banks to do business with those companies involved in the quasi-legal pot trade.
Given this momentum, it’s not difficult to see why 75 percent of Americans—including a majority of both those who support and those who oppose legalization—told Pew pollsters in February that they now believe it’s a matter of when, not if, the nation’s eight-decade-long prohibition of pot ends. The question is: Are they right?
This moment isn’t the first time that the United States appeared on the cusp of legalization. After steep gains in popular support during the early and mid-’70s, support for legalization climbed to 30 percent in 1978, only to plummet back into the teens the following decade as Baby Boomers became parents and Jimmy Carter’s pro-decriminalization administration gave way to Ronald Reagan’s war on drugs. “This was supposed to be inevitable then,” says Kevin Sabet, a legalization opponent and former Obama drug policy adviser who helped found Smart Approaches to Marijuana after leaving the administration. “No one could have predicted that [support]would have been wiped away so quickly.”
The pro-pot crowd isn’t ready to declare victory either. Ethan Nadelmann, who heads the Drug Policy Alliance and has spent decades in the reform trenches, says he’s of two minds when he thinks about the future. “On the one hand we have this extraordinary momentum,” he says. “On the other, public opinion can be fickle and marijuana is not going to legalize itself.”
While such caution is reasonable, it’s obvious that things are different now than they were 40 years ago, when then-record levels of support for legalization were good for little more than a vocal minority. It wasn’t until 2013 that a majority of Americans said for the first time that they supported making it legal to use weed. Support now stands at 54 percent in the most recent Pew poll, 23 points above where the legalization effort stood as recently as 2000 and 13 points higher than in 2010. Even those fickle Baby Boomers are back on board, with 52 percent now in favor—5 points more than that generation’s 1970s-era high. Meanwhile, each passing year brings us an electorate more familiar and less fearful of marijuana.
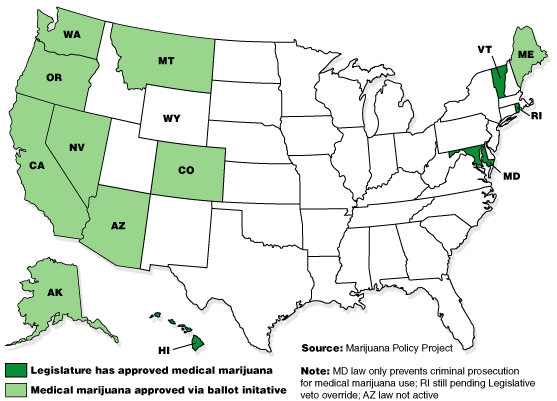
It’s not just a matter of shifting demographics. There’s also the fact that voters have increasingly gotten an up-close look at state-legal weed in the form of medical marijuana. Twenty-one states and the District of Columbia have legalized pot for medicinal purposes to varying degrees since California became the first to do so almost two decades ago. Voters in Florida are set to decide later this year whether they want to join that group, something that would give advocates their first voter-referendum victory in the South. (Florida law requires at least 60 percent support, however, making it a heavier lift than it has been in other states.)
Some pot opponents warn that medical marijuana serves as a Trojan Horse for the larger legalization movement, but that argument relies on Americans believing that the dangers of possibly legalizing recreational weed tomorrow outweigh the benefits of actually prescribing it to cancer patients and others in need today—a viewpoint shared by a diminishing number of Americans. While 54 percent of respondents told Pew they thought “the use of marijuana” should be made legal, things were more complicatedwhen the question changed from a simple yes-or-no to one where people were asked to pick between three choices: 39 percent said that pot “should be legal for personal use”; 44 percent said it “should be legal only for medicinal use”; and 16 percent said it “should not be legal.” Still, the answers to the original question—“Do you think the use of marijuana should be made legal, or not?”—suggests in an all-or-nothing environment, most Americans choose the former.
Regardless, medical marijuana has already served as stepping-stone for states that have or are considering regulating the sale and use of recreational pot. In Colorado, where retail stores opened their doors on New Year’s Day, advocates were able to point to the state’s tightly regulated medical market, approved by voters in 2000, to allay fears that the state couldn’t regulate a marijuana market from scratch. To date, Colorado regulators have delivered on those promises, building a relatively hiccup-free commercial market on the back of the medical marijuana industry. (Things in Washington, where the medical market is unregulated, have proved a good deal more complicated. Residents are still waiting for the first retail stores to open 19 months since the 2012 vote.)
Medical marijuana has become so relatively uncontroversial that late last month the House of Representatives shocked almost everyone when a bipartisan majority voted to block the Drug Enforcement Agency from pursuing medical marijuana operations that are legal under state laws. “Watershed is probably too strong of a word,” says Nadelmann of the unexpected vote for a bill that had repeatedly stalled in the same chamber for the last decade, “but it was pretty close.”
Legalization in theory is different than legalization in practice, and an unforeseen disaster in Colorado or Washington—be it from the production of hash oil or the next time a New York Times columnist overindulges in baked goods—could always affect public opinion. Colorado Gov. John Hickenlooper, a Democrat who opposed his state’s 2012 legalization initiative, for one, has warned his fellow governors to take a wait-and-see approach to their own state’s legalization efforts. But it’s looking increasingly like the voters may not be so patient if given the choice.